Introduction of timing chain tensioner
The tensioner acts on the timing belt or timing chain of the engine to guide and tighten it, so that it is always in the best tension state. It is generally divided into oil pressure and mechanical methods, which can automatically adjust the tension of timing belt and timing chain.
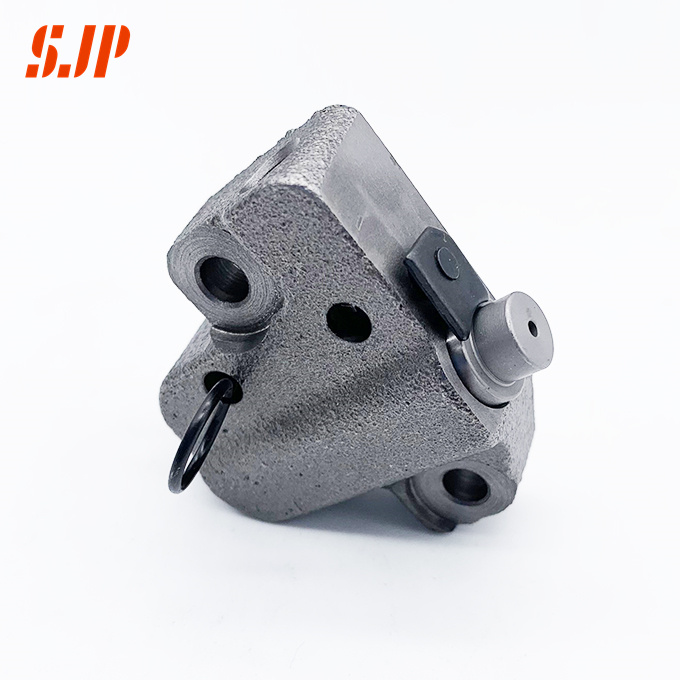

Chain tensioner action
Under the transmission of timing belt or timing chain, the camshaft drives the valve to open and close at the correct time, and cooperates with the piston to complete the four processes of intake, compression, power and exhaust. As the timing belt and timing chain will jump when running at medium and high speeds, and the timing belt will stretch and deform due to the material and force of the belt during long-term use, resulting in tooth jumping, which will lead to inaccurate gas timing, resulting in vehicle fuel consumption, weakness, detonation and other failures. When there are too many jumping teeth, the valve will collide with the upward piston and damage the engine because the valve opens too early or closes too late. In order to keep the timing belt and timing chain with proper tension, that is, to avoid tooth jumping due to looseness and damage due to tightness, there is a special tension system, which is composed of tensioner and tensioner pulley or guide rail. Tensioners provide pressure that points to the belt or chain. Tensioner pulleys are in direct contact with the timing belt, while guide rails are in direct contact with the timing chain. They apply the pressure provided by the tensioner to the belt or chain while running with the belt or chain, so that they can maintain a proper tension.
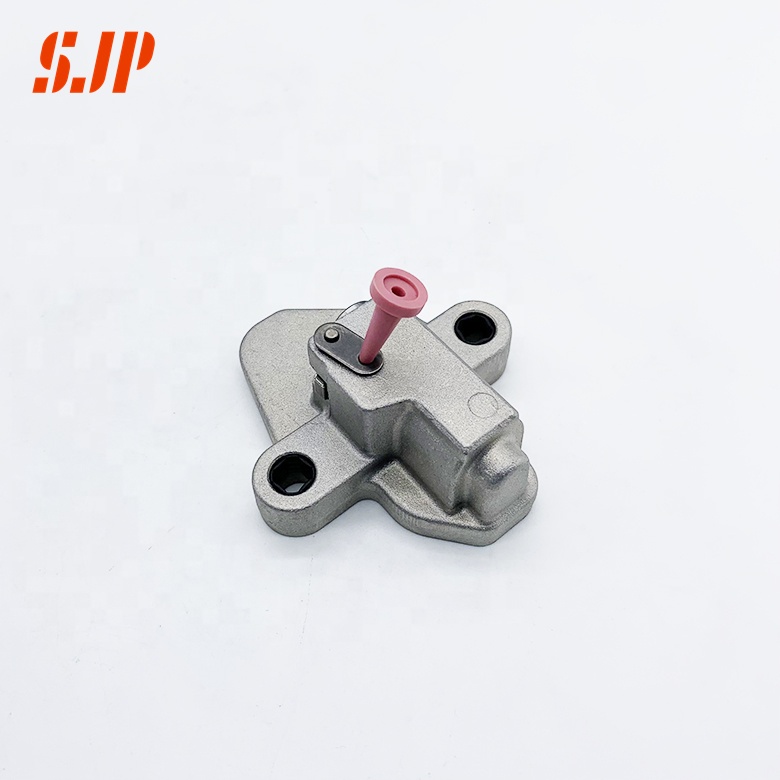

Working principle
Pull out the locking pin, and the plunger extends out of the hole under the force of the plunger spring to make the pawl at the locking plunger rotate. At the same time, the oil pressure from the engine opens the check valve, and the oil directly enters the high-pressure chamber of the tensioner assembly through the oil supply channel. The oil pressure in the high-pressure chamber is equal to that in the low-pressure chamber. The tensioning force of the tensioner is: oil pressure+spring force. Compress the plunger, the check valve is closed, and the oil in the high-pressure chamber is in a compressed state. Due to the small compressibility ratio of the oil, a large damping is formed. In the process of back pressure, the plunger damping is large, reducing the amplitude of the timing chain and transmission noise. Excess oil leaks out of the assembly through the fit clearance between the plunger and the housing hole, playing the role of overpressure protection and lubrication system.
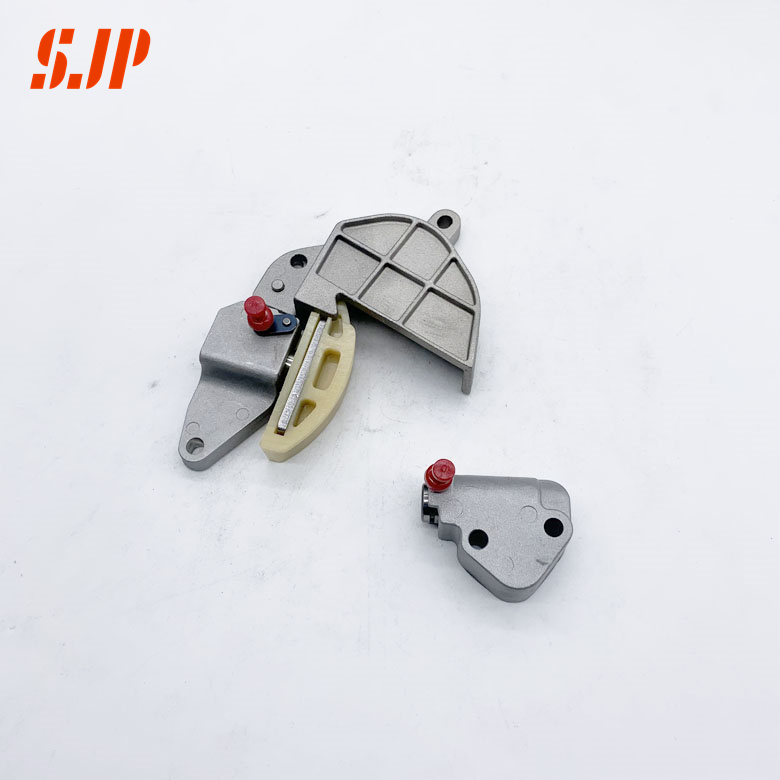

Common types of timing tensioner
1.Variable Force Tensioner
The most typical structural feature of VFT tensioner is that one large plunger and one small plunger are installed on the same plunger housing. The large plunger is in direct contact with the tensioning guide plate. The head is equipped with a one-way ball valve for oil drainage. The small plunger is connected with the tensioning guide plate through a spring pin. On the one hand, it makes use of the advantages of small plunger in rapid response, and on the other hand, it makes the system have the stability that only large plunger can have. In a sense, VFT realizes the division of the two plungers, and the control of spring force is separately placed on the small plunger+spring pin structure.
2.Spiral Spring Damper Tensioner
SSD is a mechanical tensioner, which was widely used in the early dry timing belt system and is usually composed of spring and dry friction damper. (The spring only stores energy and does not consume energy. The spring tensioner will vibrate under large external excitation, and must be used together with the damping plate.). The main difference between hydraulic tensioner and mechanical tensioner is their sensitivity to excitation frequency (engine speed). Under low-frequency excitation, the volume of the high-pressure chamber of the hydraulic tensioner changes slowly, the pressure in the chamber is relatively stable, and the oil medium can easily leak out through the damping oil groove and plunger clearance path. At this time, the damping effect of the hydraulic system is not obvious, and the overall damping characteristics are similar to those of the tensioner under the action of pure spring; Once the external excitation frequency increases and the amplitude increases, the volume of the high-pressure chamber of the hydraulic tensioner will change rapidly. At this time, the pressure in the oil chamber increases sharply, and the oil flow speed is accelerated. In the process of discharging from the chamber, a large viscous damping will be generated with the wall surface, which will significantly increase the feedback force of the tensioner. The output of the mechanical tensioner is relatively stable, and is not affected by the excitation frequency, filling medium, temperature and pressure. The design can meet the vibration reduction requirements of the engine, so as to avoid the over tension design problem to the greatest extent.
3.Internal Recirculation Tensioner
Internal circulation tensioner, also known as oil storage tensioner. Different from the ordinary hydraulic tensioner introduced at the beginning of the article, the oil storage tensioner changes the positions of the high and low pressure chambers, connects two oil chambers through a narrow damping oil passage, drains oil from the high pressure chamber to the low pressure chamber during operation, and then returns through a one-way valve to realize the recycling of most of the oil.
 Huzhou Sanjing Auto Parts Co., Ltd
Huzhou Sanjing Auto Parts Co., Ltd